
We’ve almost made it through our first week of learning remotely in Kindergarten! My hat is off to any of you who have been doing this since September! It’s been a big learning curve but thankfully, I have a wonderful community of colleagues online who have inspired me and given me confidence that I could make this work.
Today I thought I’d share a hack I figured out this week that has been a *lifesaver* for teaching live: turning my iPad into a document camera. I’ll do my best to lay out how I got this to work.
First off, these instructions are for you if you are using Google Meet for your live meeting, a PC computer, and an iPad. I could not find instructions online for this tech set up which is why I’m sharing mine here. I did find some instructions for doing this on Zoom, so I think my method will work for that meeting platform as well (maybe).
Start your meeting. I first log into my Google Meet on my PC. Then I log into the same Google Meet (with the same Google ID) on my iPad (so I am logged on twice in the meeting). It is very important to mute your microphone and turn off your video when you log in. You also have to make sure (this step is CRITICAL) that your volume controls on the side of the iPad are as low as they can go (off/muted) or else you might get feedback.
When I want to use my iPad as a document camera, I click on on the meeting controls on my iPad and choose “share screen” and “start broadcast” and then open my camera on the iPad. It will share what my camera sees with my students in the Meet.
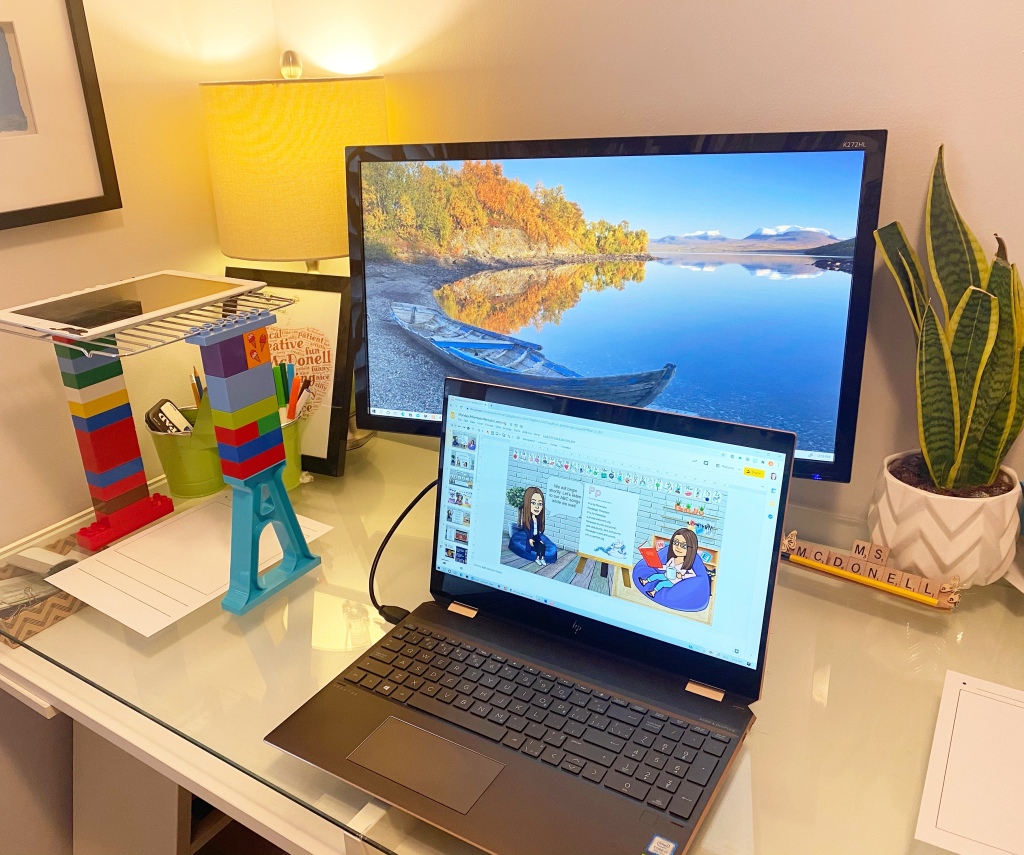
You will need a stand of some kind to put your iPad on. I built one out of Duplo and a cookie rack (yup, really. Desperate times!). The cookie rack is helpful because the camera lens fits between the bars and the bars also fit nicely on the round pegs of the Duplo, which keeps it from slipping. I taped my Duplo base to my desk for added stability. There are probably a million different ways to make a stand that will work just as well depending on what you have at home. This is the best I could come up with given the time (and I didn’t want to spend any money on it either!).

This is how it looks when I’m about to model a lesson for Writer’s Workshop:


*I should add that I had been encouraged to try using my Osmo and iPad as a doc cam, but that didn’t work for me. If you didn’t know this is possible, give it a go and see if it works for you. The Osmo was super easy to set up, but I had a long time delay when I presented it in my live meeting and it didn’t end up being what I needed. But maybe it will work better for you, and then you won’t need any Duplo or a cookie rack!
I hope my instructions were clear enough and that if you decide to try setting this up that it works for you! Wishing all of you the best as we carry forward with our remote learning journeys!
















